🔬 BPC-157 Overview
BPC-157 is a small protein fragment (peptide) made up of 15 amino acids. It is derived from a natural protective compound found in human stomach secretions.
Studies in animals show that it can significantly accelerate the healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even internal organs.
Beyond wound healing, BPC-157 helps protect the gastrointestinal tract, prevents stomach ulcers, and supports systemic repair across multiple tissue types. Research also indicates pain-relieving and angiogenic (blood-vessel-forming) properties.
Key Actions
- Promotes collagen and reticulin formation (structural fibers).
- Enhances angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels).
- Stimulates macrophage and fibroblast activity for wound repair.
- Provides organ protection and anti-ulcer effects.
- Supports nitric oxide balance and circulation.
In short, BPC-157 is a promising research compound for accelerating the body’s natural healing processes.
🧬 What Is BPC-157?
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound-157) is a synthetic version of a naturally occurring peptide found in the human digestive tract. This compound helps maintain the integrity of the stomach and intestinal lining and plays a role in regeneration and angiogenesis (new blood-vessel formation).
Core Research Areas
- Wound Healing: Promotes faster tissue regeneration.
- Blood Vessel Growth: Drives angiogenesis for nutrient delivery.
- Immune Regulation: Modulates inflammation and cytokine balance.
- Nitric Oxide Regulation: Restores vascular and circulatory function.
- Hormone Regulation: Balances neurotransmitters and gut-brain hormones.
- Neuroprotection: Supports nerve repair and brain resilience.
Molecular Details
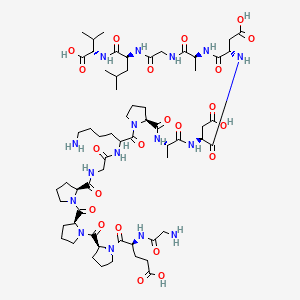
Sequence: Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Pro-Gly-Lys-Pro-Ala-Asp-Asp-Ala-Gly-Leu-Val
Formula: C62H98N16O22
Molecular Weight: 1419.56 g/mol
CAS Number: 137525-51-0
PubChem CID: 108101
Source: PubChem
🧫 BPC-157 Accelerates Wound Healing and Angiogenesis
In a study using rats with severe chemical burns, wounds treated with BPC-157 closed significantly faster than untreated wounds.
Microscopic analysis revealed thicker granulation tissue, improved re-epithelialization, and stronger collagen deposition.
In lab tests, BPC-157 also increased endothelial-cell migration and capillary-like tube formation, showing its role in angiogenesis through activation of the VEGF and ERK pathways.
References
- Huang T, Zhang K, Sun L, et al. Body protective compound-157 enhances alkali-burn wound healing in vivo and promotes proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in vitro. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015;66(2):265-272. PMID: 25995620.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Body Protective Compound-157 enhances alkali-burn wound healing in vivo and promotes proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in vitro [Internet]. PubMed Central (PMC4425239).
🩸 BPC-157 and Angiogenesis in Tendon & Soft-Tissue Healing
Executive Summary:
BPC-157 accelerates tissue repair by enhancing angiogenesis, fibroblast migration, and collagen organization. Across tendon, muscle, and connective-tissue models, it promotes regenerative healing rather than scar formation—improving strength, vascularization, and recovery even under impaired conditions.
1. Fibroblast Migration and Early Tendon Repair (Chang et al., 2011)
BPC-157 promoted fibroblast migration and protected cells from oxidative stress by activating the FAK-paxillin pathway.
Reference:
- Chang CH, Tsai WC, Lin MS, Hsu YH, Pang JHS. J Appl Physiol. 2011;110(3):774-780. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00945.2010.
2. Complete Tendon Regeneration and Structural Strength (Staresinic et al., 2003)
BPC-157 enhanced functional recovery and collagen alignment in rat Achilles-tendon transection models, producing organized parallel fibers.
Reference:
- Staresinic M, Sebecic B, Patrlj L, et al. J Orthop Res. 2003;21(6):976-983. doi:10.1016/S0736-0266(03)00110-4.
3. Restoration of Healing Under Steroid Suppression (Krivic et al., 2008)
Even with corticosteroid interference, BPC-157 restored functional recovery and increased vascularization at the tendon-bone interface.
Reference:
- Krivic A, Majerovic M, Jelic I, Seiwerth S, Sikiric P. Inflamm Res. 2008;57(5):205-210. doi:10.1007/s00011-007-7056-8.
4. Myotendinous Junction Repair (Japjec et al., 2021)
In myotendinous-junction injuries, BPC-157 led to full defect closure and functional restoration within six weeks, normalizing nitric-oxide pathways and revascularization.
Reference:
- Japjec M, Horvat Pavlov K, Petrovic A, et al. Biomedicines. 2021;9(11):1547. doi:10.3390/biomedicines9111547.
5. Angiogenic and Endothelial Pathways (Sikiric et al., 2019)
BPC-157 acts as a balanced angiogenic modulator, supporting vascular remodeling via VEGFR2–AKT–eNOS and ERK1/2 signaling.
Reference:
- Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Grabarevic Z, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019;12(3):185. doi:10.3390/ph12030185.
🧠 BPC-157 and the Immune System
BPC-157 reduces excessive inflammation and protects tissues from immune-mediated injury.
It regulates cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6), decreases swelling, and limits immune-cell overactivity.
In ischemia–reperfusion injury models, it preserved vascular integrity and reduced inflammation in organs such as liver, kidney, and lungs—likely via endothelial stabilization through the nitric-oxide system.
References
- Balenovic D, Udovicic M, Zivanovic-Posilovic G, et al. Biomedicines. 2024;12(5):573. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12050573.
- Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Gojkovic S, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(28):2972-2986. doi:10.2174/1381612827666210707093202.
💨 BPC-157 and Nitric Oxide Regulation
Nitric oxide (NO) relaxes blood vessels and improves oxygen and nutrient delivery.
BPC-157 restores balanced NO activity by stabilizing endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) while suppressing overactivation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)—reducing oxidative stress and improving microcirculation.
References
- Vukojevic J, Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(18):2009-2025. doi:10.2174/1381612824666180628125200.
- Stancic-Rokotov D, Balenovic D, Udovicic M, et al. Biomedicines. 2023;11(9):2442. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11092442.
⚖️ BPC-157 and Hormone Regulation
The enteric nervous system (ENS) communicates constantly with the brain through hormones and neurotransmitters.
BPC-157 helps normalize this gut-brain signaling, stabilizing serotonin, dopamine, oxytocin, and stress hormones such as corticosterone.
It also protects adrenal glands and supports nerve regeneration in the ENS—improving digestion, mood, and stress resilience.
References
- Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R, et al. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(2):85-97. doi:10.2174/1570159X17666191120154128.
- Gojkovic S, Balenovic D, Petrovic A, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2022;28(35):5090-5104. doi:10.3748/wjg.v28.i35.5090.
🧩 BPC-157 and Neurological Repair
Executive Summary:
BPC-157 supports nerve healing and brain protection by promoting neuronal regeneration, improving communication between brain and body, and reducing stress- or toxin-related damage.
Animal studies show axonal regrowth, reduced swelling, stabilized neurotransmitters, and improved recovery after brain or spinal-cord injury—mediated through vascular and neuronal repair pathways.
References
- Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R, et al. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(2):85-97. doi:10.2174/1570159X17666191120154128.
- Hrelec M, Balenovic D, Gojkovic S, et al. Biomedicines. 2023;11(1):240. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11010240.
- Strinic D, Petrovic A, Balenovic D, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:879020. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.879020.
🔭 Future Areas of Research
Future BPC-157 studies aim to translate animal success into human trials.
Focus areas include tendon and ligament repair, post-surgical recovery, inflammatory bowel disease, traumatic neural injury, and metabolic disorders involving vascular dysfunction.
Emerging directions include stem-cell activation, mitochondrial repair, and neuroprotection, potentially expanding its role in longevity and chronic-disease prevention.
Standardized dosing, delivery, and long-term safety data will be crucial for clinical translation.






