

Epitalon
$88.00
Research Only Purposes
- Description
- Quality Documentation
- Additional information
Description
🧬 What Is Epitalon
Epitalon (also known as Epithalon or Epithalamin) is a synthetic tetrapeptide, meaning it is a short chain composed of four amino acids — alanine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and glycine (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly). It is modeled after the natural peptide complex Epithalamin, which was originally isolated from the pineal gland of cattle.
The pineal gland is a small structure deep within the brain that regulates circadian rhythms — the 24-hour cycles governing sleep, hormone release, metabolism, and energy balance. As we age, the pineal gland’s function declines, leading to disrupted melatonin production and other downstream effects.
Epitalon is being studied for its potential to restore pineal function, support healthy aging, and protect against age-related decline. It is categorized as a geroprotector — a compound under investigation for its ability to slow the biological processes of aging.
Most foundational research has come from Russian gerontology institutes, where Epitalon has been studied since the late 20th century for its ability to:
- Extend cellular lifespan by influencing telomere biology,
- Normalize hormone regulation within the endocrine system,
- Enhance immune and cardiovascular health, and
- Protect tissues from oxidative stress and inflammatory damage.
Its research spans both molecular mechanisms (like DNA repair and gene regulation) and systemic physiology (including sleep, metabolism, and recovery).
⚗️ Molecular Structure
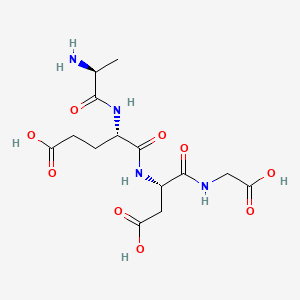
Sequence: Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly
Molecular Formula: C₁₄H₂₂N₄O₉
Molecular Weight: 390.349 g/mol
PubChem CID: 219042
CAS Number: 307297-39-8
Source: PubChem
🔬 Epitalon: Key Research Areas and Potential Benefits
1. Cellular Aging and Telomere Biology
Epitalon has been shown in cell culture and animal models to activate telomerase, an enzyme that maintains and elongates telomeres — the DNA-protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that naturally shorten with each cell division. Shortened telomeres trigger cellular senescence (loss of growth and repair capacity).
By activating telomerase, Epitalon may delay cellular aging and extend the replicative lifespan of normal cells.
Why this matters: Preserving telomere length is one of the key goals in longevity science, as telomere erosion contributes to tissue degeneration and biological aging.
Reference:
- Khavinson VK, Bondarev IE, Butyugov AA. Peptide regulation of gene expression: a systematic study. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;994(1):170-177. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb03175.x
2. Sleep Regulation and Melatonin Rhythms
The pineal gland produces melatonin, the hormone that governs the body’s internal clock. As melatonin output decreases with age, circadian rhythms and sleep quality deteriorate.
Experimental evidence indicates that Epitalon can restore melatonin synthesis and normalize daily secretion cycles, thereby improving both sleep and overall hormonal balance in aging subjects.
Why this matters: Proper circadian rhythm regulation influences sleep quality, mood, metabolism, and immune health — all of which deteriorate with age.
Reference:
- Khavinson VK, Korkushko OV, Zapadnyuk IP, Wozniak W. Peptide regulation of pineal gland function in aging. Vopr Onkol. 2002;48(2):200-208.
3. Immune System Function
In aging models, Epitalon has been reported to enhance immune cell regeneration and reactivate thymic function, leading to improved T-cell activity and systemic immune balance.
This modulation may help offset immunosenescence — the gradual weakening of immune defenses that occurs with age.
Why this matters: A balanced immune system defends against infection while preventing chronic inflammation, one of the leading drivers of aging.
Reference:
- Khavinson VK, Lezhava TA, Monaselidze JR, et al. Peptide epitalon activates telomerase and prolongs the proliferative ability of human somatic cells in vitro. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2003;135(5):519-522. doi:10.1023/A:1025421317071
4. Apoptosis and Cellular Surveillance
Apoptosis is the natural, programmed death of cells that are damaged or no longer needed. Epitalon has been studied for its ability to modulate apoptosis, support DNA repair mechanisms, and regulate gene expression linked to cellular quality control.
By influencing these pathways, Epitalon may help cells repair themselves instead of prematurely self-destructing, supporting longevity at the cellular level.
Reference:
- Khavinson VK, Vityuk OV. DNA-binding regulatory peptides: synthesis, properties, and biological significance. Usp Fiziol Nauk. 2000;31(1):3-16.
5. Retinal and Ocular Health
Epitalon has been evaluated for its protective effects on retinal cells and its ability to reduce oxidative damage in the eye — both major contributors to age-related vision decline.
In experimental models, it reduced markers of oxidative stress and preserved the structure of photoreceptor cells, which are essential for clear vision.
Reference:
- Khavinson VK, Malinin VV. Peptide regulation of aging: results of experimental and clinical studies. Aging (Milano). 2000;12(3):149-160. doi:10.1007/BF03339808
6. Antioxidant Mechanisms
Epitalon demonstrates antioxidant properties, reducing lipid peroxidation and neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) in tissues.
This helps protect cell membranes from oxidative damage and supports the balance between free radical generation and antioxidant defense.
Why this matters: Chronic oxidative stress accelerates tissue aging and inflammation. Compounds that reduce oxidative damage may protect organ integrity and function.
Reference:
- Anisimov VN, Khavinson VK, Alimova IN, et al. Inhibitory effect of the synthetic pineal peptide epitalon on colon carcinogenesis induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine in rats. Cancer Lett. 1999;145(1-2):135-141. doi:10.1016/S0304-3835(99)00228-4
7. Mitochondrial Function and Physical Endurance
Mitochondria are the energy-producing organelles within cells. Research suggests that Epitalon can help preserve mitochondrial function and redox balance (the balance between oxidation and reduction reactions critical for metabolism).
Improved mitochondrial efficiency translates into better cellular energy output, which may contribute to physical endurance and metabolic stability in aging organisms.
Reference:
- Khavinson VK, Lezhava TA, Malinin VV. Peptide epitalon activates telomerase and prolongs the proliferative ability of human somatic cells in vitro. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2003;135(5):519-522. doi:10.1023/A:1025421317071
8. Cardiovascular Research
Preclinical data suggest Epitalon can improve arterial elasticity, blood pressure control, and vascular integrity through its antioxidant and circadian-normalizing actions.
These findings indicate possible benefits in reducing vascular stiffness and supporting healthy blood flow during aging.
Reference:
- Khavinson VK, Malinin VV. The development of peptide preparations for the prevention and treatment of aging-associated pathologies. Curr Aging Sci. 2008;1(3):263-270. doi:10.2174/1874609810801030263
9. Reproductive Aging
Studies have examined how Epitalon influences the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis, the hormonal system that controls reproduction.
Results suggest it may help normalize gonadal hormone feedback loops and reduce age-related fertility decline in experimental models.
Reference:
- Khavinson VK, Vityuk OV. Peptide regulation of gonadal function in aging. Adv Gerontol. 2000;6:11-18.
10. Neuroprotective Models
Epitalon has also been examined for its neuroprotective properties in aging and neurodegeneration models.
By reducing oxidative stress and improving gene regulation, Epitalon may help protect neurons, preserve synaptic integrity, and delay cognitive decline associated with aging.
Reference:
- Khavinson VK, Vityuk OV. Peptide regulation of gene expression: a systematic study. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;994(1):170-177. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb03175.x
🚀 Future Areas of Research and Clinical Focus
- Clinical Efficacy in Sleep Disorders:
- Larger, controlled human trials are needed to confirm Epitalon’s effectiveness in restoring melatonin rhythms and improving sleep in older adults.
- Molecular Pathway Mapping:
- Further studies are exploring how Epitalon affects gene expression, protein synthesis, and epigenetic regulation beyond telomerase activation.
- Long-Term Cardiovascular Markers:
- Longitudinal research will help clarify whether Epitalon’s antioxidant and circadian effects translate into measurable cardiovascular protection.
- Combined Therapies:
- Researchers are testing combinations of Epitalon with other bioregulatory peptides (like thymic peptides, GHK-Cu, and BPC-157) and senolytics to determine synergistic anti-aging effects.
Additional information
| CAS | 307297-39-8 |
|---|---|
| MG | 25 |
| Brand | Sovereign Health and Performance |








