

GHK-Cu
$69.00
Research Only Purposes
- Description
- Quality Documentation
- Additional information
Description
🧬 What Is GHK-Cu?
GHK-Cu (glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine–copper) is a naturally occurring tripeptide—a molecule made of three amino acids—that has a powerful ability to bind copper ions (specifically copper(II)). It was first discovered in human plasma in the 1970s and is found throughout the body, including in saliva and urine. However, levels of GHK-Cu decline significantly with age.
GHK-Cu is often described as a “remodeling peptide” because of how it manages tissue repair and renewal. Its main biological role is to act as a copper chaperone—it transports and delivers copper to cells that need it. Copper is essential for many enzymes responsible for:
- Collagen and elastin production (for firm, resilient skin and connective tissue)
- Antioxidant protection, including enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD)
- Cellular energy metabolism and repair processes
GHK-Cu therefore helps regulate both the breakdown of damaged tissue and the formation of healthy new tissue, giving it importance in research on wound healing, anti-aging, hair growth, and even gene expression regulation.
⚗️ Molecular Structure
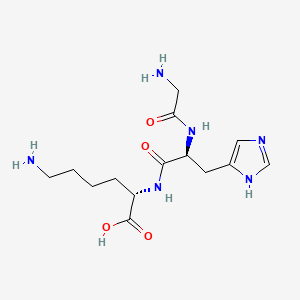
Source: PubChem
Sequence: Gly-His-Lys·Cu·xHAc
Molecular Formula: C₁₄H₂₃CuN₆O₄
Molecular Weight: 401.91 g/mol
PubChem CID: 73587
CAS Number: 89030-95-5
⚡ Key Actions
GHK-Cu has been studied for its broad and multi-layered biological activity. Key effects include:
- Delivers bioavailable copper to activate critical copper-dependent enzymes
- Stimulates collagen, elastin, and glycosaminoglycan production, helping skin, tendons, and connective tissues regenerate
- Accelerates wound healing and supports remodeling of old or fibrotic tissue
- Regulates matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) to balance tissue breakdown and rebuilding
- Reduces inflammation by lowering cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and TGF-β
- Provides antioxidant protection by boosting copper-dependent enzymes
- Supports hair follicle health and dermal papilla cell activity
- Influences gene expression related to repair, regeneration, and cell protection
- Improves tissue resilience in skin, muscle, and joint structures
- May support cognitive and neural protection through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms
🔬 Key Research Areas and Potential Benefits
1. Wound Healing, Tissue Regeneration, and Scar Remodeling
GHK-Cu speeds up wound healing and helps remodel old or damaged tissue. It promotes the formation of new collagen and elastin while regulating enzymes (MMPs) that break down excess or poorly formed scar tissue, replacing it with stronger, healthier structures.
Reference:
- He J, Zhang X, Ma H. The naturally occurring peptide GHK reverses age-related fibrosis by modulating myofibroblast function. Aging Pathobiol Ther. 2021;3(3):144-154.
2. Skin Biology and Aging Models
GHK-Cu activates fibroblasts, the cells responsible for creating collagen and elastin, and increases skin elasticity and firmness. Research also shows that combining GHK-Cu with hyaluronic acid boosts collagen IV production, strengthening the skin’s foundation layer.
Reference:
- Jiang J, Wu D, Wang Y, et al. Synergy of GHK-Cu and hyaluronic acid on collagen IV upregulation via fibroblast and ex vivo skin tests. Biomed Res Int. 2023;2023:9483120. doi:10.1155/2023/9483120
3. Inflammatory Modulation
Inflammation slows healing and contributes to aging. GHK-Cu helps calm excessive inflammation by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and TGF-β, while protecting against oxidative stress. This dual action supports tissue recovery and longevity.
Reference:
- Pickart L, Vasquez-Soltero JM, Margolina A. The human tripeptide GHK-Cu in prevention of oxidative stress and degenerative conditions of aging: implications for cognitive health. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:324832. doi:10.1155/2012/324832
4. Hair Follicle Research
Studies in human hair follicle models show that GHK-Cu can stimulate dermal papilla cells (DPCs), which control the hair growth cycle. The peptide also supports improved microcirculation and scalp health, creating a more favorable environment for hair regeneration.
Reference:
- Pyo HK, Yoo HG, Jung SY, et al. The effect of tripeptide-copper complex on human hair growth in vitro. Arch Pharm Res. 2007;30(7):834-839. doi:10.1007/BF02977612
5. Cellular Protection from UV Radiation
UV exposure increases oxidative stress and DNA damage. GHK-Cu enhances the skin’s antioxidant gene expression and helps cells survive and repair after UV radiation. It essentially supports the skin’s built-in defense system.
Reference:
- Pickart L, Vasquez-Soltero JM, Margolina A. GHK-Cu may prevent oxidative stress in skin by regulating copper and modifying expression of numerous antioxidant genes. Cosmetics. 2015;2(3):236-247. doi:10.3390/cosmetics2030236
6. Antioxidant Activity
By providing copper to antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), GHK-Cu enhances the body’s ability to neutralize free radicals and protect tissues from oxidative damage. This is especially valuable in skin and connective tissue health.
Reference:
- Gruchlik A, Chodurek E, Dzierżewicz Z. Influence of selected peptides and their copper complexes on antioxidant enzyme activities in human skin fibroblasts. Adv Dermatol Allergol. 2010;27(1):29-35.
7. Oncological Research (Exploratory)
Preclinical studies have examined GHK-Cu’s impact on cell proliferation and apoptosis (programmed cell death). Results suggest it may influence gene expression that helps control abnormal growth, though this research is still early and exploratory.
Reference:
- Pickart L, Vasquez-Soltero JM, Margolina A. Regenerative and protective actions of the GHK-Cu peptide in the light of the new gene data. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):1987. doi:10.3390/ijms19071987
8. Cognitive Function and Neurobiology
GHK-Cu may help protect brain cells and support cognitive function by influencing gene expression related to synaptic repair and neuroinflammation. It may increase brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which supports neuron health and plasticity.
Reference:
- Pickart L, Vasquez-Soltero JM, Margolina A. The effect of the human peptide GHK on gene expression relevant to nervous system function and cognitive decline. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;55(1):145-160. doi:10.3233/JAD-160633
9. Joint and Connective Tissue Research
GHK-Cu has shown promise in healing ischemic or inflamed tissues—areas with poor blood flow and oxygen. In animal wound models, it accelerated healing and reduced inflammation, suggesting applications for joint, tendon, and soft-tissue repair.
Reference:
- Canapp SO, Farese JP, Schulz KS, et al. The effect of copper peptide (GHK-Cu) on the healing of ischemic wounds. Vet Surg. 2003;32(6):531-537. doi:10.1053/jvet.2003.50066
10. Muscle and Connective Tissue Recovery
In muscle injury and fibrosis models, GHK-Cu supports tissue remodeling and reduces oxidative damage, leading to improved muscle regeneration and recovery.
Reference:
- Pickart L, Vasquez-Soltero JM, Margolina A. Regenerative and protective actions of the GHK-Cu peptide in the light of the new gene data. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):1987. doi:10.3390/ijms19071987
🚀 Future Areas of Research and Clinical Focus
- Optimizing Delivery Systems
- Research is focusing on ways to enhance GHK-Cu’s absorption and stability using liposomes or nanoparticles for topical or transdermal use.
- Neuroprotective Applications
- Deeper study of GHK-Cu’s effects on the brain could clarify how it supports cognitive longevity and neural repair.
- Chronic Wound Healing (e.g., Diabetic Ulcers)
- Its ability to promote angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation) and collagen synthesis makes it a candidate for hard-to-heal wounds.
- Fibrosis and Scarring Across Organs
- GHK-Cu’s gene-regulating actions may help limit fibrosis not just in skin, but in organs like the lungs, liver, and heart.
- Combination Therapies
- Ongoing exploration pairs GHK-Cu with other regenerative peptides (such as BPC-157, TB-4, or GHK variants) to amplify tissue repair benefits.
Additional information
| CAS | 89030-95-5 |
|---|---|
| MG | 100 |
| Brand | Sovereign Health and Performance |








