

- Description
- Quality Documentation
- Additional information
Description
💉 What Is Gonadorelin (GnRH)
Gonadorelin is the synthetic form of the natural hormone called Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) — the body’s master regulator of the reproductive and hormonal system known as the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal (HPG) axis.
This small peptide (a chain of ten amino acids, also called a decapeptide) is released by the hypothalamus, a brain region that coordinates many automatic processes, including hormone release.
When Gonadorelin enters the bloodstream, it travels a very short distance to the anterior pituitary gland, where it binds to GnRH receptors on specialized cells. This binding triggers the pulsatile (wave-like) release of two key hormones:
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH) — which stimulates testosterone production in men and ovulation in women.
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) — which supports sperm production and ovarian follicle maturation.
The unique feature of Gonadorelin is that its effects depend entirely on how it’s administered:
- When given in pulses, it mimics the body’s natural rhythm and stimulates fertility and hormone production.
- When given continuously, it actually suppresses LH and FSH release — shutting down reproductive hormone signaling.
Because of this dual behavior, Gonadorelin and its analogues are used extensively in hormone research, infertility treatments, and oncology to manipulate hormone levels safely and predictably.
⚗️ Molecular Structure
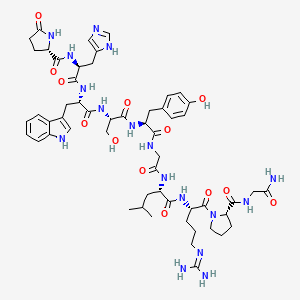
Sequence: Pyr-His-Trp-Ser-Tyr-Gly-Leu-Arg-Pro-Gly
Molecular Formula: C55H75N17O13
Molecular Weight: 1182.311 g/mol
PubChem CID: 638793
CAS Number: 9034-40-6
Source: PubChem
🔬 Gonadorelin: Key Research Areas and Clinical Applications
1. Endocrine Regulation
Gonadorelin is a cornerstone molecule in research on the HPG axis, the system that controls reproductive hormone production.
By triggering pulsatile release of LH and FSH, it helps regulate sex steroid hormones like testosterone and estradiol.
Reference:
- Kaiser UB, Sabbagh E, Chen SR, Wierman ME. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone regulation of pituitary gonadotropin gene expression. Endocr Rev. 1997;18(5):605-645. doi:10.1210/edrv.18.5.0315
2. Reproductive Function Models
Gonadorelin has been widely used in both men and women to study how the brain controls fertility. In women, it’s used to induce ovulation when the hypothalamus fails to release GnRH naturally (a condition called hypothalamic amenorrhea). In men, it supports sperm production by stimulating FSH and LH release.
Reference:
- Klingman LM, Zacur HA. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone for induction of ovulation in women with hypothalamic amenorrhea. Fertil Steril. 1987;48(1):23-28. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(16)59378-8
3. Pituitary Function Testing
One of Gonadorelin’s earliest and most reliable uses is the GnRH stimulation test, used to evaluate pituitary gland health. After administration, doctors measure the resulting surge in LH and FSH. The size and timing of this surge reveal whether the pituitary is functioning normally.
Reference:
- Bercu BB, Hung W. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone testing in children. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1987;16(2):333-350. doi:10.1016/S0889-8529(18)30332-8
4. Hormonal Deficiency and Hypogonadism
In individuals with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (HH) — a condition where the hypothalamus or pituitary fails to produce enough GnRH or LH/FSH — Gonadorelin is used to restore natural hormone signaling through rhythmic, pulsatile infusion. This treatment can restore fertility in both men and women.
Reference:
- Crowne EC, Shalet SM. Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone therapy in hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Arch Dis Child. 1990;65(3):337-340. doi:10.1136/adc.65.3.337
5. Fertility Preservation in Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
When men use external testosterone, the body’s natural LH and FSH production often shuts down, suppressing sperm production. Research explores Gonadorelin as a way to preserve fertility during TRT by mimicking the natural GnRH pulse that keeps the testes active.
Reference:
- Cavender RK, Fairbanks W. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone and its analogues in the management of male infertility. Fertil Steril. 1993;60(4):723-730. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(16)56218-5
6. Oncological Research: Prostate Cancer
Long-acting GnRH agonists (derivatives of Gonadorelin) are used in prostate cancer treatment to suppress testosterone production.
While short-term pulsatile GnRH increases hormone levels, continuous exposure causes the pituitary to desensitize and shut down LH/FSH release — effectively lowering testosterone to castrate levels, which slows tumor growth.
Reference:
- Schally AV, Kastin AJ. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists for suppression of pituitary-gonadal function. Endocr Rev. 1987;8(1):60-70. doi:10.1210/edrv-8-1-60
7. Oncological Research: Fertility Preservation in Breast Cancer
In premenopausal women undergoing chemotherapy, GnRH analogues (like continuous Gonadorelin) can temporarily suppress ovarian function. This protects the ovaries from damage, helping preserve fertility after treatment.
Reference:
- Moore HCF, Unger JM, Phillips KA, et al. Goserelin for ovarian protection during breast-cancer adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(10):923-932. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1413204
8. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
Gonadorelin and its analogues are critical tools in IVF and ART protocols.
By precisely timing GnRH agonists and antagonists, researchers can control LH surges, prevent premature ovulation, and improve synchronization for egg retrieval and implantation success.
Reference:
- Fauser BCJM, van Heusden AM. Manipulation of human ovarian function: physiological concepts and clinical consequences. Endocr Rev. 1997;18(1):71-106. doi:10.1210/edrv.18.1.0287
9. Endometriosis and Hormone-Sensitive Disorders
Continuous use of Gonadorelin analogues suppresses estrogen production, helping treat endometriosis and other estrogen-driven conditions. By lowering estrogen levels, it reduces the growth of misplaced endometrial tissue, easing pain and inflammation.
Reference:
- Olive DL, Schwartz LB. The clinical use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists in the treatment of endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1989;44(8):547-555. doi:10.1097/00006254-198908000-00002
10. Developmental Endocrinology and Puberty
Gonadorelin is used to both stimulate delayed puberty (when administered in pulses) and suppress premature puberty (when given continuously). Its role in regulating LH and FSH release makes it vital for understanding developmental hormone control.
Reference:
- Carel JC, Eugster EA, Rogol A, Ghizzoni L, Palmert MR. Treatment of central precocious puberty by GnRH agonists. Endocr Dev. 2013;24:198-210. doi:10.1159/000342547
🚀 Future Areas of Research and Clinical Focus
- Non-Invasive Delivery:
- Developing oral, nasal, or transdermal GnRH delivery systems to replace injectable formulations, improving patient compliance and precision dosing.
- Reversible Contraceptive Development:
- Designing short-acting GnRH antagonists that offer reliable, hormone-free contraception for both sexes.
- Neuroprotective and Cognitive Research:
- Exploring GnRH receptors in the brain and spinal cord, which may play roles in neuroprotection, stress response, and cognition independent of reproduction.
- Precision Pulsatile Therapy:
- Using programmable pumps and smart dosing algorithms to more accurately replicate natural GnRH rhythms in fertility and aging research.
Additional information
| CAS | 12079884 |
|---|---|
| MG | 10, 2 |
| Brand | Sovereign Health and Performance |









