MOTS-c
$99.00
Research Only Purposes
- Description
- Quality Documentation
- Additional information
Description
🧬 What is MOTS-c
MOTS-c (Mitochondrial Open Reading Frame of the 12S rRNA-C) is a 16–amino-acid peptide encoded by the mitochondrial genome (mtDNA), making it a rare example of a peptide produced directly by mitochondria rather than nuclear DNA. It belongs to a small family of mitochondrial-derived peptides (MDPs) that act as intracellular messengers to regulate metabolism and stress responses.
MOTS-c can move from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm and even the nucleus, where it influences genes related to energy production, nutrient sensing, and cellular defense.
Its best-known mechanism involves activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) — the cell’s master energy regulator — which enhances glucose utilization, fat oxidation, and overall metabolic balance.
Because of its central role in maintaining energy homeostasis and stress adaptation, MOTS-c has become a major focus of research in longevity science, metabolic health, mitochondrial function, and exercise physiology.
🔬 Molecular Structure
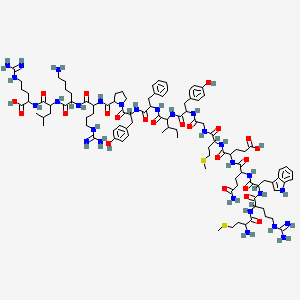
Sequence: Met-Arg-Trp-Gln-Glu-Met-Gly-Tyr-Ile-Phe-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg
Molecular Formula: C₁₀₁H₁₅₂N₂₈O₂₂S₂
Molecular Weight: 2174.64 g/mol
PubChem SID: 255386757
CAS Number: 1627580-64-6
Synonyms: Mitochondrial Open Reading Frame of the 12S rRNA-C, MT-RNR1
Source: PubChem
⚡ Key Actions
Research has identified several key physiological effects of MOTS-c:
- Activates AMPK, increasing glucose uptake and metabolic flexibility
- Promotes fat oxidation and reduces lipid accumulation
- Enhances mitochondrial function and ATP energy production
- Improves insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle
- Increases exercise performance and endurance
- Reduces inflammation and regulates cytokine signaling
- Supports neuroprotection and cognitive function
- Preserves lean muscle mass and combats sarcopenia
- Mitigates oxidative stress and improves redox balance
- May contribute to longevity by maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis
🔬 MOTS-c: Key Research Areas and Potential Benefits
1. Metabolic Regulation
MOTS-c enhances glucose metabolism by activating AMPK, promoting the use of glucose for energy, and improving cellular metabolic flexibility. Preclinical studies suggest it helps maintain blood glucose balance under conditions of stress or nutrient excess.
Reference:
- Lee C, Zhan L, Nakhuda A, et al. The mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c regulates metabolism and energy homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2015;21(3):443-454. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2015.02.010
2. Lipid Oxidation and Body Composition
Animal studies show that MOTS-c promotes fat oxidation and reduces adiposity by enhancing mitochondrial fatty acid metabolism. It has been investigated as a potential tool for improving body composition and energy expenditure.
Reference:
- Sikandar A, Mushtaq F, Anwar S, et al. Therapeutic potential of MOTS-c in obese and diabetic mice. FASEB J. 2017;31(1_Suppl):890.18.
3. Exercise Performance and Endurance
MOTS-c has been shown to improve exercise capacity and mitochondrial efficiency. By enhancing ATP generation in muscle cells, it may increase endurance and reduce fatigue.
Reference:
- D’Souza S, Ryu D, Zhang L, et al. MOTS-c reverses obesity and improves glucose homeostasis in mice fed a high-fat diet. J Endocrinol. 2017;232(3):399-412. doi:10.1530/JOE-16-0424
4. Aging and Mitochondrial Health
MOTS-c supports mitochondrial homeostasis and helps cells resist metabolic stress. Research suggests it can reduce markers of cellular aging and improve overall mitochondrial resilience.
Reference:
- Sood S, Torres SJ, Mathai ML, et al. MOTS-c: a novel mitochondrial-encoded regulator of skeletal muscle function and insulin sensitivity. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(11):3542-3551. doi:10.1002/jcb.26049
5. Insulin Sensitivity
In rodent models, MOTS-c enhances insulin action and glucose uptake in skeletal muscle through AMPK-dependent signaling. This positions it as a potential therapeutic target for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Reference:
- Lee C, Zhan L, Nakhuda A, et al. Cell Metab. 2015;21(3):443-454. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2015.02.010
6. Inflammation and Cytokine Modulation
MOTS-c reduces inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6 and protects vascular tissue from inflammatory damage in high-glucose environments.
Reference:
- Fetterman JL, Chaudhuri C, Wallace EK, et al. MOTS-c prevents endothelial cell inflammation and dysfunction in a high-glucose environment. FASEB J. 2019;33(1_Suppl):165.1.
7. Cognitive and Neural Health
Neuroprotective studies indicate that MOTS-c supports mitochondrial function in neurons, reduces oxidative stress, and may protect against neurodegenerative processes such as those seen in Alzheimer’s disease.
Reference:
- Cen X, Chen S, Zhang L, et al. Mitochondrial peptide MOTS-c as a novel neuroprotective agent against Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(11):7309-7324. doi:10.1007/s12035-019-1615-8
8. Muscle Preservation and Sarcopenia
MOTS-c has been shown to preserve lean muscle mass and maintain mitochondrial function in aging muscle. This makes it a promising focus in research on sarcopenia (age-related muscle wasting) and physical decline.
Reference:
- Kim S, Seo S, Kim K, et al. MOTS-c prevents age-related sarcopenia by regulating mitochondrial function and metabolism. FASEB J. 2021;35(S1):e21376. doi:10.1096/fasebj.2021.35.S1.e21376
9. Cellular Energy and Fatigue
By improving mitochondrial efficiency and ATP generation, MOTS-c supports energy balance under metabolic or physical stress, helping reduce fatigue and improve vitality.
Reference:
- Lee C, Zhan L, Nakhuda A, et al. Cell Metab. 2015;21(3):443-454. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2015.02.010
10. Oxidative Stress and Redox Balance
MOTS-c activates antioxidant defense pathways such as Nrf2/HO-1 and reduces oxidative damage to endothelial and muscle cells. This contributes to its protective role in aging and metabolic health.
Reference:
- Hwang J, Jeong HM, Kim JS, et al. MOTS-c attenuates oxidative stress-induced endothelial cell injury through activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;149:223-231. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.11.021
❤️ Heart Health and Cardiovascular Research
Although not a primary research area, MOTS-c’s effects on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and inflammation may indirectly benefit cardiovascular health. Animal studies suggest it may protect against metabolic cardiotoxicity by improving mitochondrial resilience.
Reference:
- Reynolds L, Park M, Kim RA, et al. The mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c protects against cardiotoxicity in a high-fat diet model. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022;11(11):e024227. doi:10.1161/JAHA.121.024227
🚀 Future Areas of Research and Clinical Focus
- Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes:
- Large-scale human trials are expected to evaluate MOTS-c as a therapeutic candidate for improving insulin sensitivity and metabolic control in obesity and diabetes.
- Sarcopenia and Mobility:
- Ongoing studies will assess MOTS-c’s potential to preserve mitochondrial quality and prevent age-related muscle weakness in older adults.
- Delivery Mechanism Optimization:
- Future research aims to develop oral, nasal, or transdermal MOTS-c delivery systems to enhance bioavailability and long-term adherence for metabolic applications.
✳️ Summary
MOTS-c represents one of the most exciting mitochondrial discoveries of the past decade — a naturally encoded peptide that acts as both a metabolic regulator and a cellular stress signal.
By activating AMPK, improving mitochondrial performance, and promoting resilience against oxidative and inflammatory damage, it stands at the intersection of metabolism, performance, and longevity research.
Additional information
| CAS | 1627580-64-6 |
|---|---|
| MG | 10 |
| Brand | Sovereign Health and Performance |