- Description
- Quality Documentation
- Additional information
Description
🧬 What is NAD⁺
NAD⁺ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a vital coenzyme present in every cell of the body. It exists in two forms — the oxidized NAD⁺ and the reduced NADH — and serves as one of the body’s primary carriers of hydrogen and electrons.
At its core, NAD⁺ is essential for cellular energy production, redox balance, and communication between the nucleus and mitochondria. Without NAD⁺, cells cannot efficiently convert nutrients into ATP, repair DNA, or regulate gene expression.
In simpler terms: NAD⁺ acts like a rechargeable battery inside every cell, transferring energy wherever it’s needed to sustain fundamental biological processes.
As NAD⁺ levels naturally decline with age, researchers are increasingly focused on its role in metabolic health, aging, and cellular resilience.
🔬 Molecular Structure
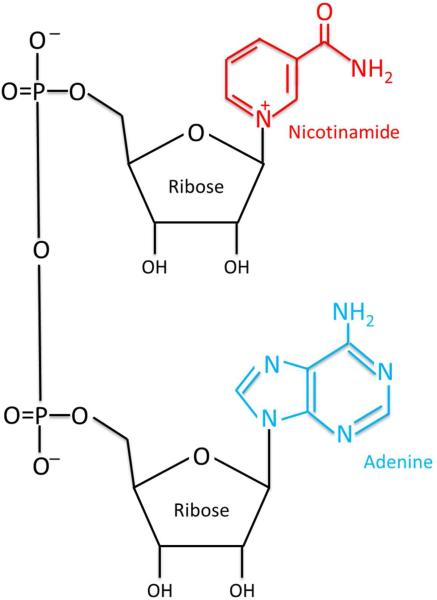
Chemical Formula: C₂₁H₂₇N₇O₁₄P₂
Molecular Weight: 663.43 g/mol
Molecular Type: Dinucleotide coenzyme composed of two nucleotides joined by phosphate groups — one containing an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.
PubChem CID: 5893
CAS Number: 53-84-9
Synonyms: β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, DPN⁺, Coenzyme I
Source: PubMed
⚡ Key Actions
Research on NAD⁺ has been shown to:
- Act as an essential electron carrier in energy production
- Serve as a cofactor for over 500 enzymatic reactions
- Regulate sirtuin enzymes that influence aging and DNA repair
- Support mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative capacity
- Modulate inflammation and circadian rhythm
- Facilitate vascular health and nitric oxide signaling
In general terms: NAD⁺ helps cells carry out countless chemical reactions that sustain life, from producing energy to managing stress and maintaining balance within tissues.
🔬 NAD⁺: Key Research Areas and Potential Benefits
1. Energy & Redox Biology
NAD⁺ functions as a hydrogen and electron carrier essential for glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. These pathways convert carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into ATP — the chemical energy that powers all cellular processes.
Maintaining NAD⁺ levels ensures balanced redox states (oxidation-reduction) and prevents metabolic slowdown associated with fatigue, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging.
In plain terms: when NAD⁺ is present in sufficient amounts, cellular energy systems operate efficiently — a process researchers study to better understand how cells respond to stress, exertion, and age-related decline.
Reference:
- Ying W. NAD⁺/NADH and NADP⁺/NADPH in cellular functions and cell death regulation: lessons from animal models. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1787(9):1352-1362. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.05.018
2. Aging & Sirtuin Activity
NAD⁺ is the required cofactor for sirtuin enzymes (SIRT1–SIRT7), which regulate gene expression, mitochondrial biogenesis, stress response, and lifespan. Low NAD⁺ levels impair sirtuin activity, contributing to cellular aging and metabolic decline.
Boosting NAD⁺ in animal studies has been associated with enhanced longevity, improved stress tolerance, and delayed onset of age-related diseases.
Explained simply: sirtuins are sometimes described as the body’s “longevity switches,” and NAD⁺ serves as their energy source — a mechanism scientists explore to understand how cells adapt and maintain balance under stress.
Reference:
- Imai S-I, Guarente L. NAD⁺ and sirtuins in aging and disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2014;24(8):464-471. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2014.04.002
3. DNA Repair & Genomic Stability
NAD⁺ serves as a substrate for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs), enzymes that detect and repair DNA strand breaks. When DNA damage occurs, PARPs consume NAD⁺ to facilitate repair and maintain genomic stability.
Chronic NAD⁺ depletion can compromise DNA integrity and accelerate cellular senescence, making PARP-NAD⁺ interactions a major focus of research in cancer biology and aging.
Put another way: NAD⁺ supports the molecular machinery that corrects genetic damage — one reason scientists study its role in cellular maintenance and long-term genomic stability.
Reference:
- Bai P, Cantó C. The role of PARP-1 and PARP-2 enzymes in metabolic regulation and disease. Cell Metab. 2012;16(3):290-295. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.06.016
4. Mitochondrial Health & Function
Mitochondria depend on NAD⁺ to drive the electron transport chain — the process that generates ATP. Studies show that NAD⁺ levels regulate mitochondrial biogenesis, mitophagy, and oxidative capacity.
Restoring NAD⁺ in experimental models has been shown to reverse mitochondrial dysfunction, enhance endurance, and support metabolic resilience during aging.
In simpler language: researchers view NAD⁺ as a key regulator of the cell’s “power grid,” helping mitochondria produce energy efficiently and maintain performance even under stress.
Reference:
- Gomes AP, Price NL, Ling AJ, et al. Declining NAD⁺ induces a pseudohypoxic state disrupting nuclear-mitochondrial communication during aging. Cell. 2013;155(7):1624-1638. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.037
5. Cellular Signaling: Inflammation & Circadian Rhythm
NAD⁺ modulates immune and circadian pathways through enzymes such as CD38 and SIRT1. These enzymes regulate inflammatory cytokines and the expression of circadian clock genes.
In preclinical models, optimizing NAD⁺ metabolism has been shown to reduce chronic inflammation, improve sleep-wake cycle regulation, and restore energy rhythm synchronization across tissues.
Plainly explained: scientists are studying how NAD⁺ influences the body’s “daily rhythms” — from energy balance to inflammation control — by acting as a timekeeper molecule that helps coordinate biological cycles.
Reference:
- Sahar S, Sassone-Corsi P. Regulation of metabolism and the circadian clock by NAD⁺ and sirtuins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(9):613-623. doi:10.1038/nrm3366
6. Potential Sexual Health Benefits
Although NAD⁺ is not intended for human therapeutic use, researchers have investigated its role in mitochondrial energy production and vascular signaling. Experimental data suggest that NAD⁺’s influence on endothelial nitric oxide synthesis and circulatory function could support sexual health parameters such as libido, erectile function, and reproductive vitality.
These findings remain strictly preclinical and are currently limited to animal or cell-based models.
In general terms: NAD⁺ is being studied for how it affects blood vessel performance and energy systems — areas that indirectly relate to reproductive and vascular health.
Reference:
- de Picciotto NE, Gano LB, Johnson LC, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation reverses vascular dysfunction and oxidative stress with aging in mice. Aging Cell. 2016;15(3):522-530. doi:10.1111/acel.12461
🚀 Future Areas of Research and Clinical Focus
- Longevity and Cellular Health:
- Ongoing studies are exploring NAD⁺ augmentation (via NMN or NR precursors) to extend healthspan and enhance tissue resilience.
- Metabolic Disorders:
- Research continues into NAD⁺’s potential role in treating obesity, insulin resistance, and fatty liver disease.
- Neurodegeneration:
- Investigations aim to determine whether restoring NAD⁺ can protect against age-related cognitive decline and diseases such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s.
- Vascular and Mitochondrial Medicine:
- Studies are assessing NAD⁺’s potential to support endothelial repair, circulation, and mitochondrial restoration in cardiovascular and metabolic aging.
In summary: the research community continues to explore NAD⁺ as a central molecular link between energy metabolism, longevity, and resilience — not as a therapy, but as a way to better understand the biology of aging itself.
✳️ Summary
NAD⁺ is the central molecule of cellular metabolism and repair, acting as the cell’s energy broker and a regulator of sirtuins, PARPs, and mitochondrial enzymes.
Its decline with age affects nearly every biological system — from energy and immunity to DNA stability and vascular function.
As research continues, NAD⁺ remains at the forefront of investigations into longevity, metabolic health, and cellular rejuvenation.
Put simply: maintaining or restoring NAD⁺ in laboratory settings helps researchers model how cells stay strong, efficient, and responsive — shedding light on how the body preserves balance and vitality over time.
Additional information
| CAS | 53-84-9 |
|---|---|
| MG | 500 |
| Brand | Sovereign Health and Performance |